Levers
A lever is a rigid bar that truns around point called fulcrum. Various forces may act on the lever at the same time. When the forces acting on opposite ends of a lever are equal, we say the lever is in equilibrium. We can express this mathematically as the Law of the Lever:
F x d = R x r
A HAND CRANK
It has two parts, one is connected to a rotating shaft and the other forms a handle. We can use a hand crank to apply force at a distance from the axis of the shaft. It has the Law of the Lever.
 |
| Class 2 lever |
PULLEYS AND COMPOUND OF PULLEYS SYSTEMS
In a system of pulleys, equilibrium between the forces depends on the path that the rope follows.
PULLEYS
A pulley is a wheel that rotates around an axis and has a groove. We use this mechanism to apply less force. There are two basic pulleys:
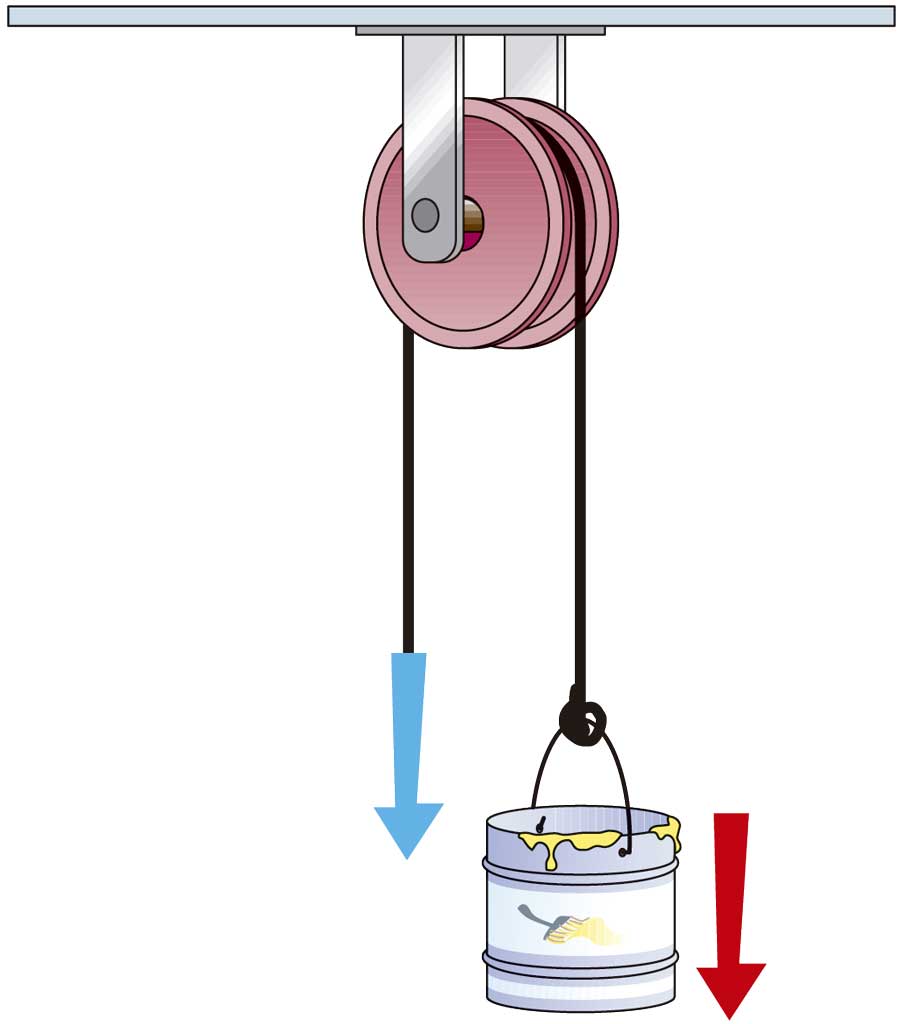 |
| Fixed pulley (F=R) |
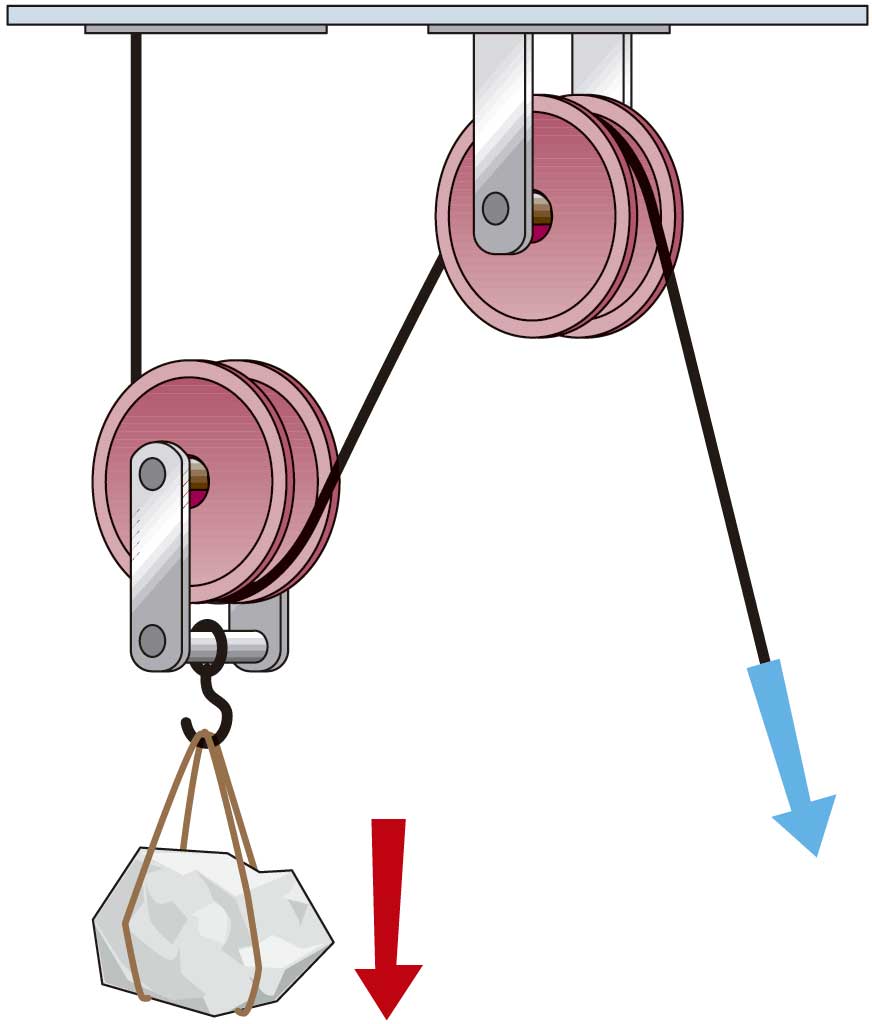 |
| Movable pulley (F=R/2) |
COMPOUND PULLEY SYSTEMS
This is a special combination of fixed and movable pulleys.The more pulleys we have, the mechanism is more complex, but it is easier to lift the load.
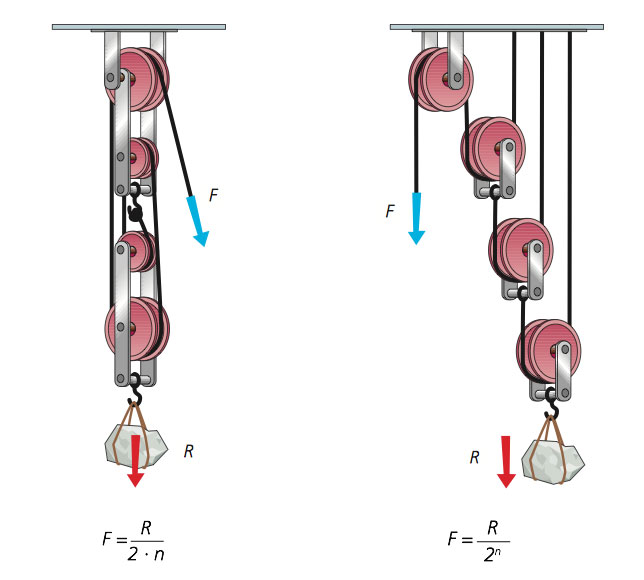 |
| Vertical and Exponential systems |
| Horizontal System |
