Rotary transmission systems put two rotating elements into contact. These mechanisms have two purposes:
⇒Transferring rotary force to an input location to another location.
⇒Changing the rotary speed by using rotating elements of different sizes.
There are various mechanisms:
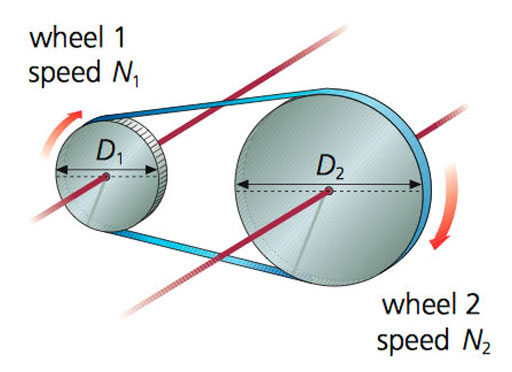 |
| Pulleys with belts |
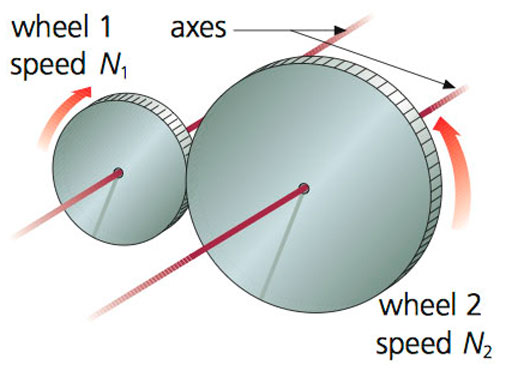 |
| Friction wheels |
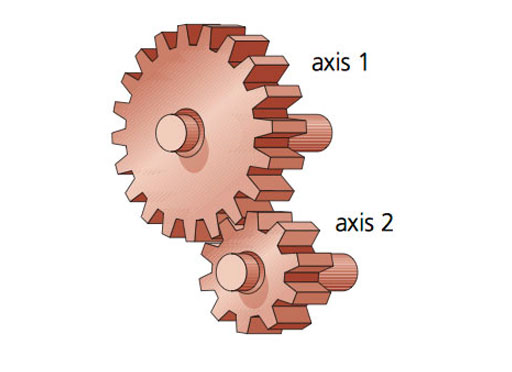 |
| Interlocking gears |
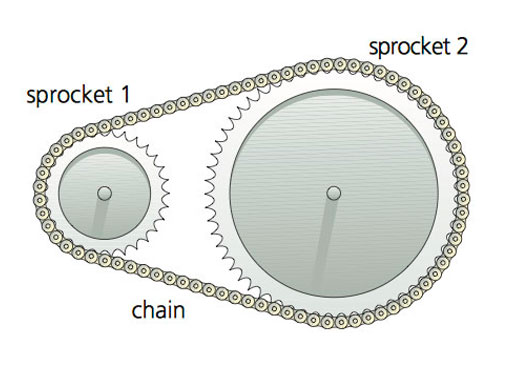 |
| Sprockets with chains |
Here, the most reliable mechanism is the interlocking gears, because they don't slip easily.
CHANGES IN SPEED
We can increase, decrease and make constant the speed with these systems:
  |
| Decreasing and Increasing speed system |
 |
| Cosntant speed system |
SPEED RATIOS
The relationship between the speeds of the two wheels is inversely proportional to their sizes.
N2/N1=D1/D2
The relationship is called the ratio of transmission, where N is the speed of relation and D is the diameter of the wheel.
BELT DRIVES AND GEAR TRAINS

We can change the direction of the rotation by using belts in different possicions or different axis.
WORM DRIVE
A worm drive reduces the speed of rotary system very well. It has two parts: a worm shaft and a worm gear. The shaft has more than one groove. Each groove interlocks with one of the worm gear. This mechanism is not reversible.
BELT DRIVES AND GEAR TRAINS

-Wheel 1 turns wheel 2, wich moves faster because it is smaller. If wheel 1 makes 1 rotation, wheel 2 makes 1.5 rotations.
-Wheel 2 and wheel 3 are connected to the same axis, so they turn together.
-Wheel 3 turns wheel 4, wich moves faster because it is smaller. If wheel 3 makes 1.5 rotations, wheel 4 makes 3 rotations (1.5x2=3)
N4/N1=D1XD3/D2XD4
CHANGES IN DIRECTION AND ROTATIONS
 |
| Parallel axes |
| Perpendicular axes |
| Different posicion of the belts |
 |
| Crossed axes |
WORM DRIVE
A worm drive reduces the speed of rotary system very well. It has two parts: a worm shaft and a worm gear. The shaft has more than one groove. Each groove interlocks with one of the worm gear. This mechanism is not reversible.

No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario